What are the advantages and disadvantages of solid-state batteries?
A disruptive technology is promised before the end of the decade by manufacturers: solid-state battery. What are its advantages?
We have to wait and see. In short, here is the advice we might give at Mobiwisy if you’re hesitating between buying outright or leasing with or without commitment your electric car. Technology is evolving so rapidly that obsolescence of a vehicle is faster than ever. With a century invested in thermal engines, manufacturers have thrown all their strengths into electric vehicles for less than a decade. And progress is astonishing. What will it be in 5, 10, 15 or 20 years?
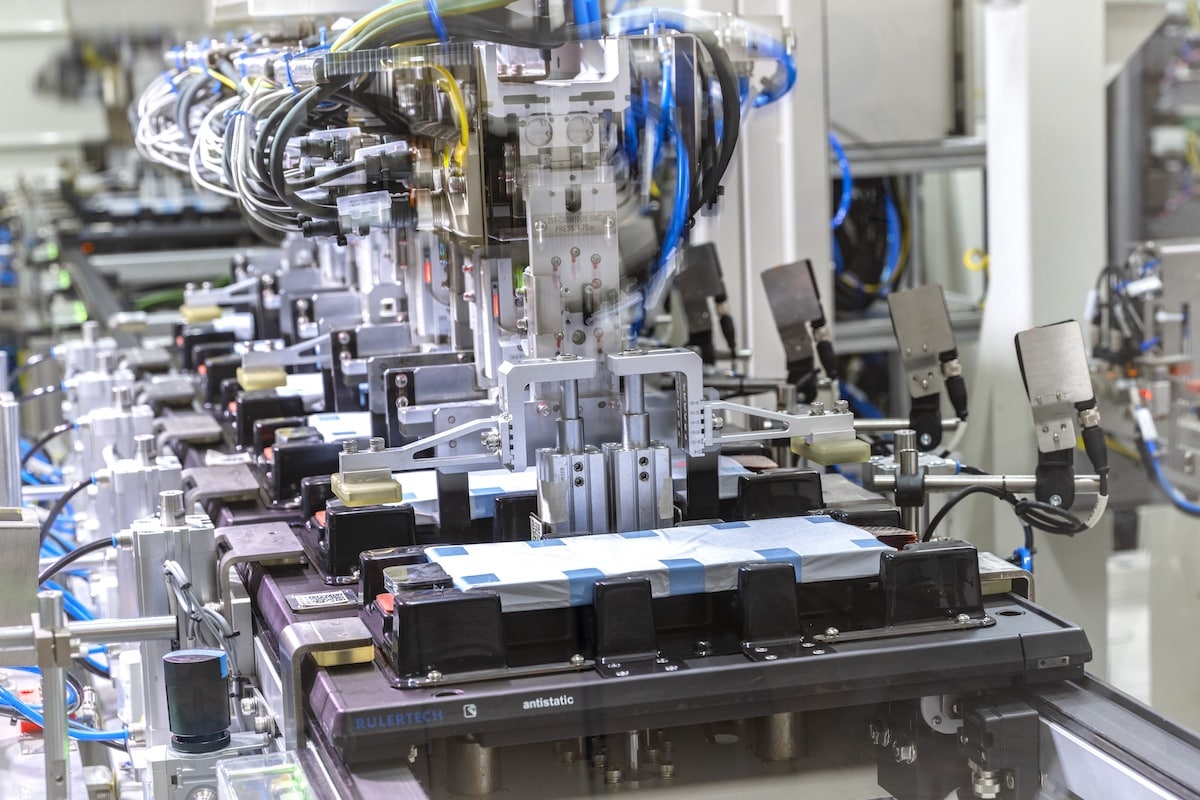
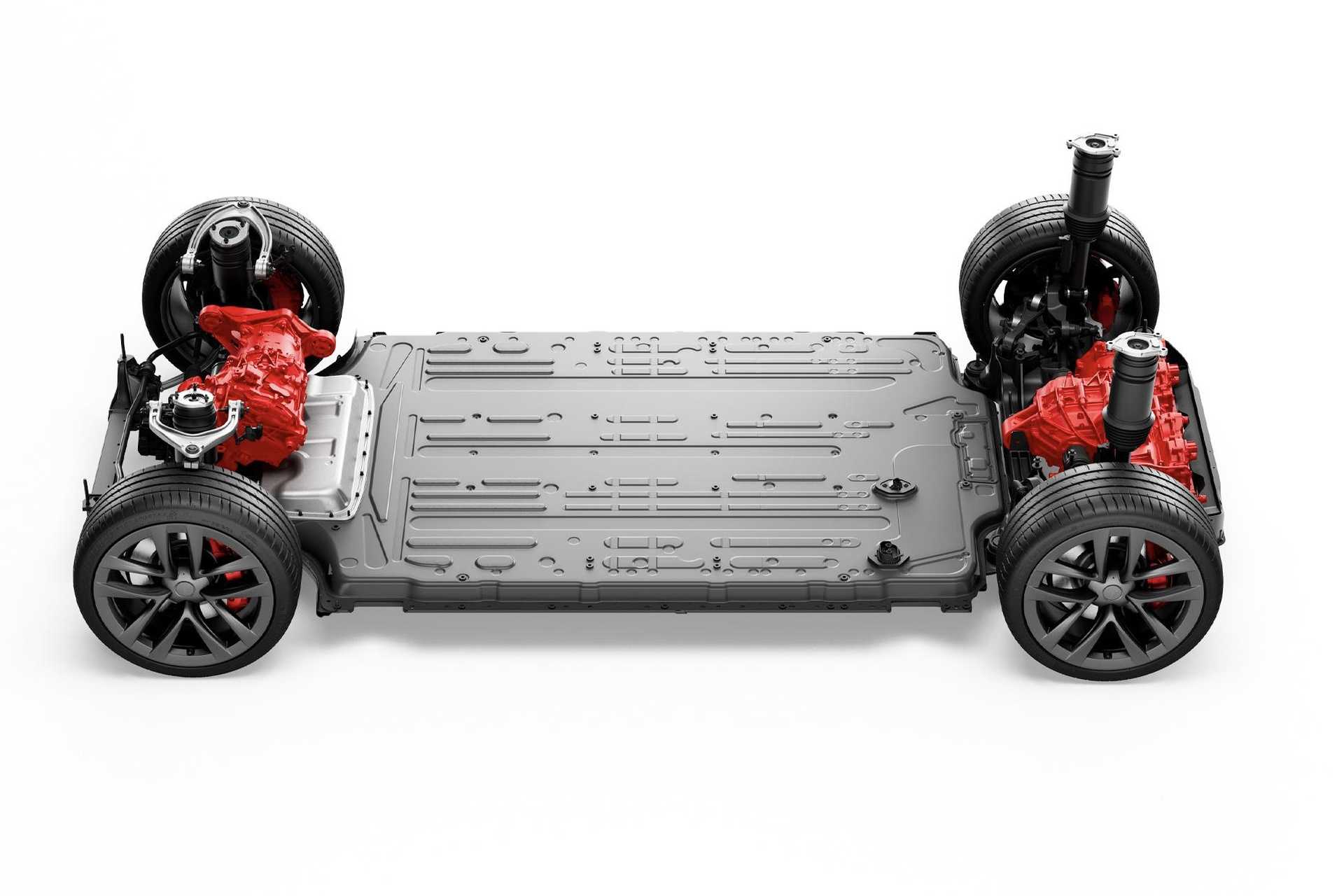
The battery, and thus energy storage, is at the heart of the issue. Density, weight, raw material costs—the battery remains the core organ of a car. Hydrogen will remain too complicated to deploy, so batteries will stay central to the future. A new technology, called “Solid,” is approaching.
The advantages of solid-state batteries:
- Higher energy density: Solid electrolyte batteries can store more energy per unit of volume or weight than traditional lithium-ion batteries, potentially increasing the range of electric vehicles.
- Faster charging times: Solid batteries can potentially be charged more quickly than current batteries, reducing wait times for users.
- Improved safety: Solid electrolytes are less likely to cause fires or explosions because they do not contain flammable liquids.
- Longer lifespan: These batteries could last longer because they are less susceptible to degradation than lithium-ion batteries.
- Wide operating temperature range: Solid batteries can operate effectively over a broader temperature range, making them more reliable in extreme climates.
- Reduced environmental impact: They could be more environmentally friendly, due to the use of less toxic materials and easier recyclability.
The disadvantages of solid-state batteries:
- High production costs: Manufacturing solid batteries is often more expensive than producing traditional lithium-ion batteries due to specialized materials and processes required.
- Interface issues: Interfaces between solid electrodes and solid electrolyte can be unstable, potentially leading to rapid degradation and performance loss.
- Challenges in large-scale manufacturing: Mass production of solid batteries is complex. The technology is still in early development stages, making large-scale, cost-effective production difficult.
- Limited energy density: Although theoretically higher, the practical energy density of solid batteries may be limited by current materials and manufacturing techniques.
- Durability issues: Solid batteries can be sensitive to durability problems, notably dendrite growth (metallic structures) that can pierce the solid electrolyte and cause short circuits.
- Compatibility with existing infrastructure: Integrating solid batteries into existing electric vehicles may require significant modifications, as their operation differs from traditional lithium-ion batteries.
- Temperature limitations: While generally more stable at high temperatures, some solid batteries may have reduced performance in low temperatures.
As we have seen, many challenges remain to fully master this technology, which nonetheless is set to become dominant. It is the course of history.
READ ALSO: Renault Scenic: soon an offer with battery leasing?
This page is translated from the original post "Quels sont les avantages et désavantages de la batterie solide ?" in French.
We also suggestthese articles:
Also read