Electric Car: What Are the Different Charging Ports?
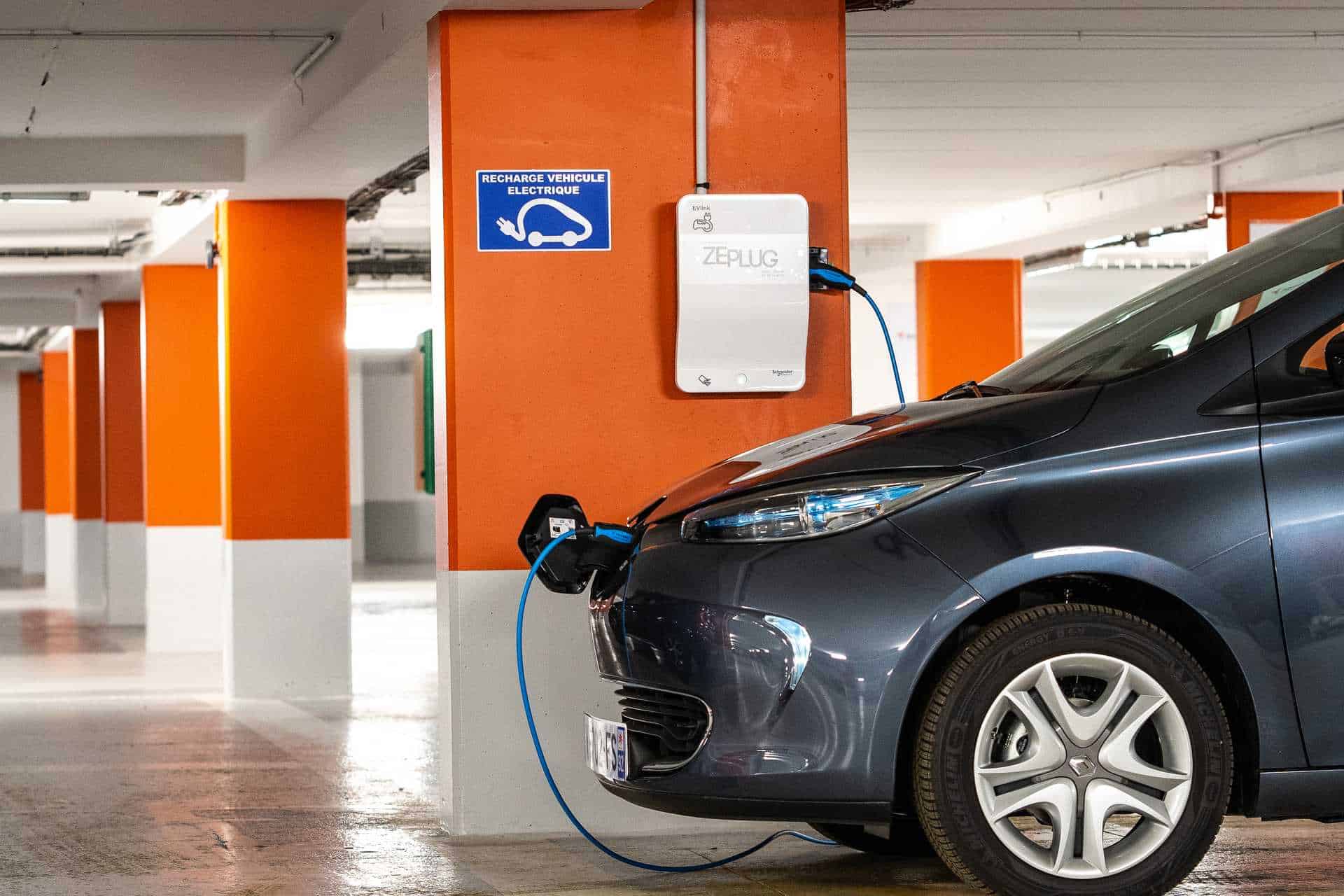

Alternating or Direct Current, Type 2 or CCS, or at Home, here’s our guide to understanding all the different electric vehicle charging connectors.
Refueling a combustion engine or fuel-powered car involves a single operation: filling up at the pump station. With an electric vehicle, it’s very different. You can recharge at home or on public charging stations, using various outlets and power levels. Discover everything you need to know about electrical sockets and recharging your electric car.
Slow Charging Connectors
In France, several types are available for electric cars. They operate on alternating current, the same as your home or apartment supply. The cable is provided here, either standard or optional, connected directly from your vehicle to the outlet. Here are the main types to distinguish in 2023:
- Standard 230 V domestic socket. Used for slow charging at no extra cost. However, it is advisable to install a proper electrical system to prevent overheating risks. Power ranges from 1.8 to 2.3 kW, requiring dozens of hours for a full charge.
- Green’Up. Also intended for slow charging. With a power of 3.7 kW, it is safer than a standard domestic outlet because it has a protection device, supporting up to 20 A. Charging time can be halved compared to a traditional socket. Approximate cost: €300.
- Wallbox or wall-mounted box. Named after the company Wallbox, it is a box that allows charging power up to about 7.4 kW (single-phase), four times faster than a standard socket. A compatible Type 2 cable is required. This type of outlet costs several hundred euros, excluding installation.
Accelerated and Fast Charging Connectors

We recommend charging your electric vehicle using a slow charger. However, faster charging may be necessary due to time constraints. Fast or rapid chargers use three-phase alternating current, or even direct current. They are often found in parking lots, on public roads, or at highway stations. Here are the different types for your vehicle:
- Type 2. Used for accelerated charging. Available on Wallbox units with single-phase, or faster via 11 or 22 kW three-phase supply. Compatible with most cars in Europe, offering faster charging than domestic outlets.
- Combined Charging System (CCS). Used for fast and ultra-fast charging, now the standard in Europe. The cable is directly attached to the station and must be plugged into your electric vehicle. It supports even faster charging than Type 2. Providing direct current, its power is often 50 kW (fast charging) or over 150 kW (ultra-fast). Charging from 10% to 80% typically takes between 30 minutes and 1 hour, depending on the model.
- CHAdeMO. A rapid charging standard from Japan. Mainly used by Nissan or older models like Citroën C-ZERO or Peugeot i0n. It was once widespread on public stations but is now becoming rarer, with a maximum power of 43 kW.
- Tesla connector. Proprietary format of the Tesla brand. Used on early Tesla models like Model S and X. It is possible to charge using a standard socket with the supplied cable, but a Tesla-specific adapter is required for Type 2 or CCS stations.
Which car for which socket or charging power?
It’s useful to know that not all electric cars have the same charging capacity or use the same sockets. Some rare models do not come with a standard CCS Combo socket, such as the Renault ZOE or the Dacia Spring. Other vehicles lack an onboard charger capable of handling 11 or 22 kW three-phase alternating current.
Finally, even if a car supports fast charging, its maximum power varies by model. A Fiat 500 tops out at 50 kW, the Peugeot e-208 at 100 kW, and the Porsche Taycan leads the market at 270 kW.
Read also: Electricity prices 2023, what is the cost of recharging an electric car?
This page is translated from the original post "Voiture électrique : quelles sont les différentes prises de recharge ?" in French.
We also suggestthese articles:
Also read