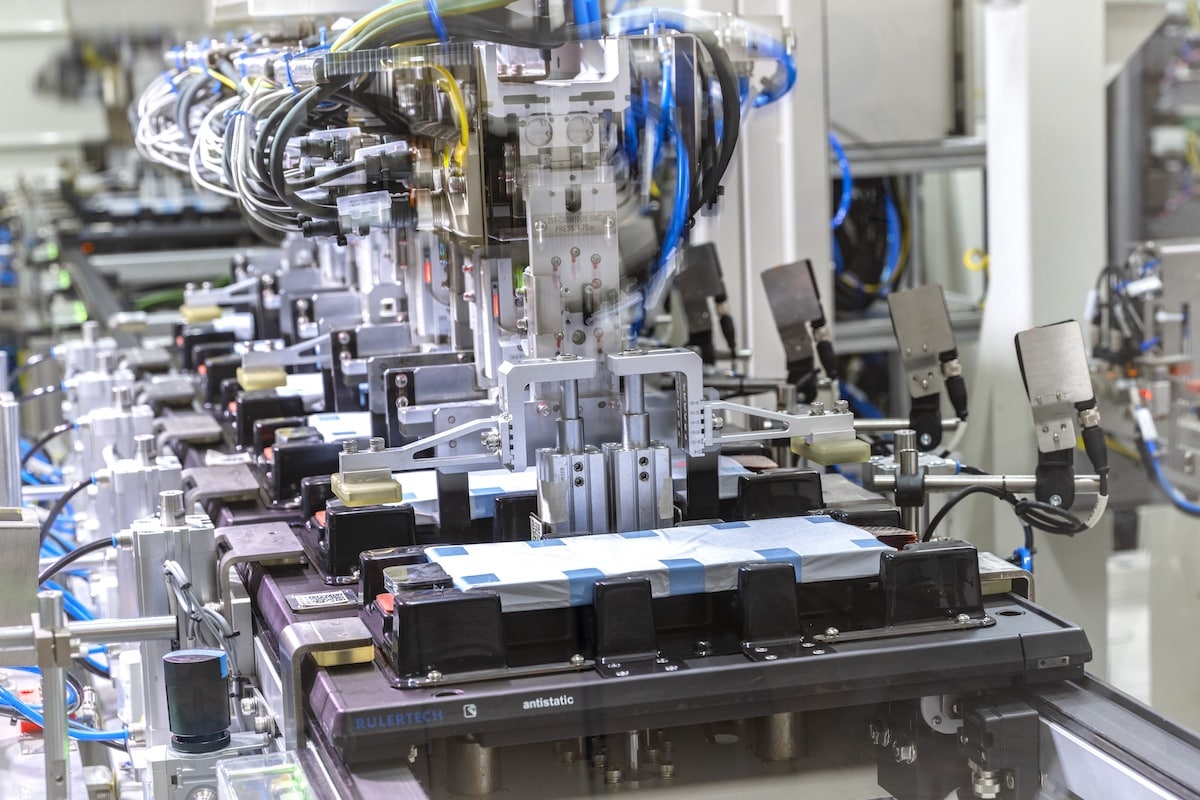
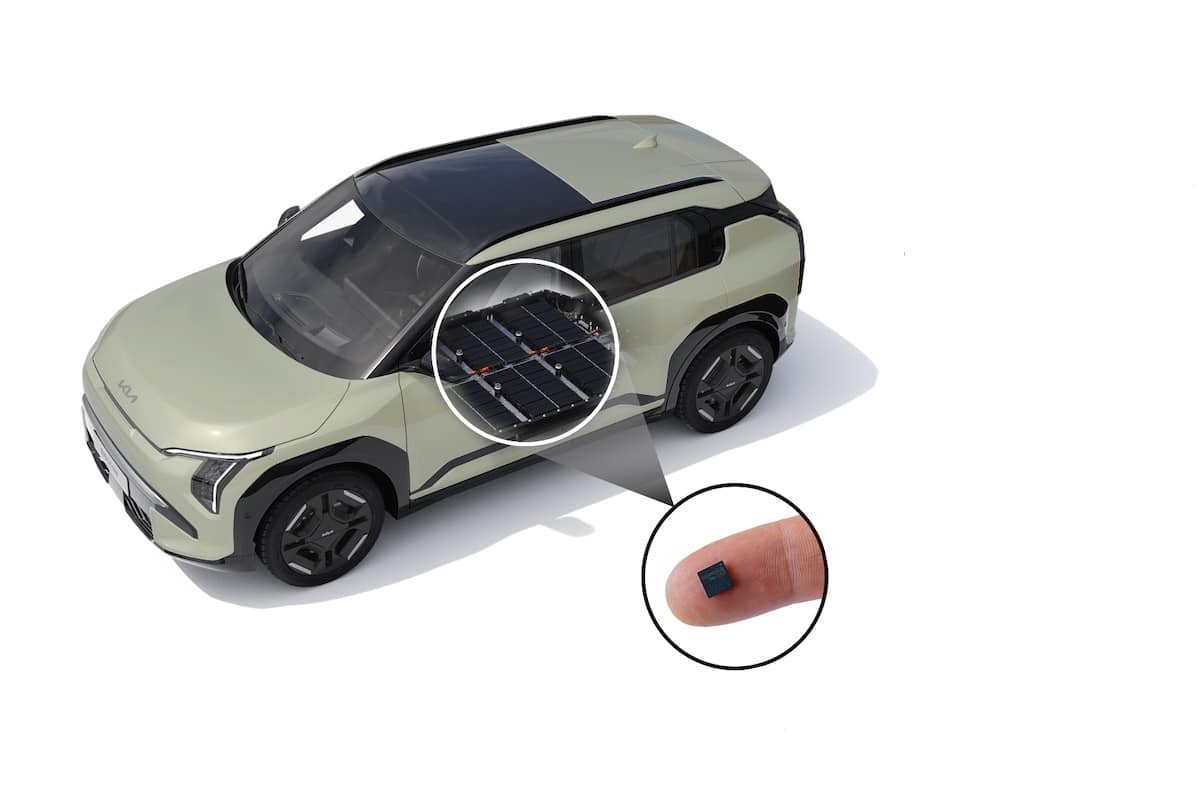
Stellantis invests in Lithium-Sulfur batteries with Lyten
Stellantis has chosen to invest in the American company Lyten and its Lithium-Sulfur battery technology to develop sustainable automotive mobility.
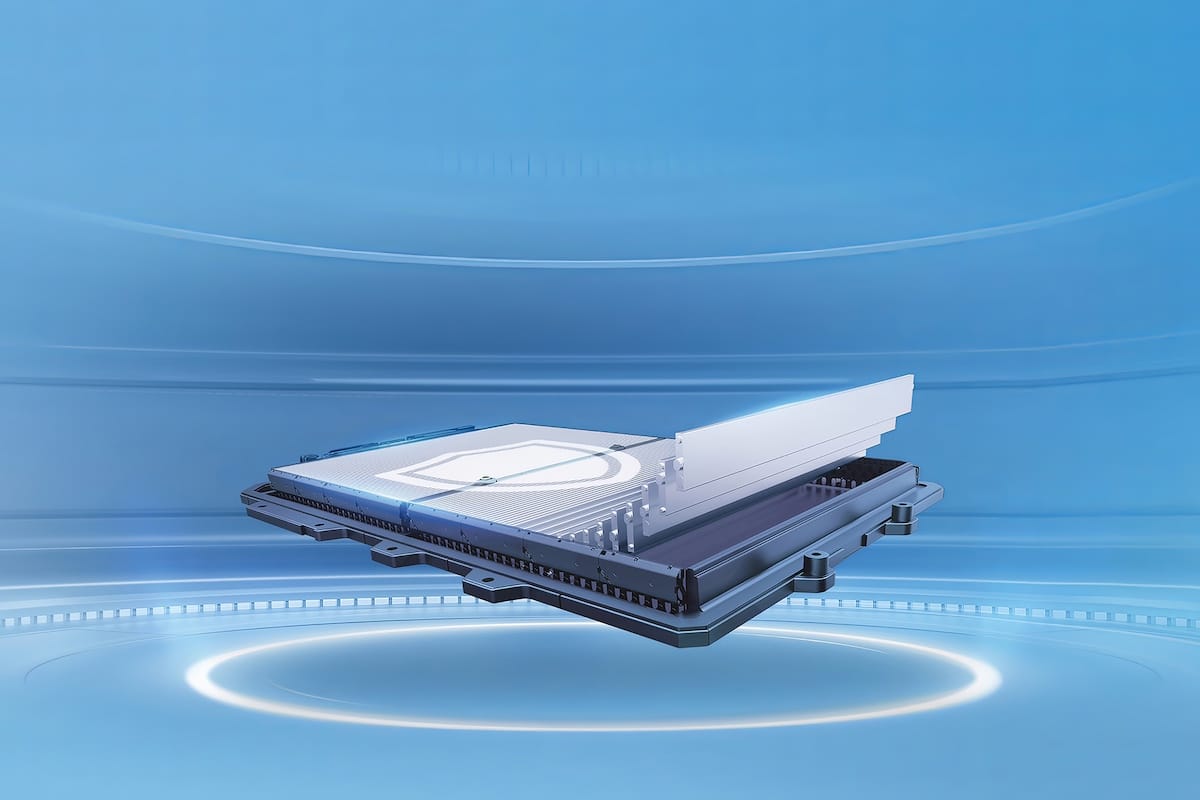
Stellantis’ venture capital fund, Stellantis Ventures, invests in the American company Lyten, which has Lithium-Sulfur battery technology. According to Stellantis, this partnership will help accelerate the commercialization of Lyten’s 3D Graphene in the transportation sector.
The Stellantis Ventures fund is part of Stellantis and seeks innovative companies or technologies that could eventually improve the brand’s vehicles. Therefore, they have chosen to invest in Lithium-Sulfur (Li-S) batteries, specifically LytCell. This technology has the potential for higher energy density than traditional lithium-ion batteries.
Lithium-Sulfur Battery, an Emerging Technology
The European Commission already published an article on this topic in 2020, highlighting its benefits. The battery appears to be lighter, less expensive, and more energy-dense. Indeed, the Lithium-Sulfur battery does not use materials such as nickel, cobalt, or manganese. Instead, it replaces these materials with sulfur, which is cheaper and less rare.
Moreover, according to Futura Sciences, lithium-sulfur batteries have a higher energy density (up to 2,600 Wh/kg) compared to current lithium-ion batteries (300 Wh/kg) used in electric vehicles. Therefore, Stellantis’ investment will support further development of this technology, potentially making batteries more efficient.
However, the European Commission also highlighted some issues. Two major concerns are: the shuttle effect and chemical deposits that can damage the battery.
Lithium-sulfur batteries consist of chemical elements that react with each other. It is the interaction between these elements that produces energy and electricity. Unfortunately, their interaction can form chemical deposits that degrade the battery over time. During charging and discharging cycles (shuttle effect), the battery’s capacity decreases. The chemical reactions may also cause a short circuit (or fire risk).
This is why passengers are advised to keep their lithium-ion portable batteries (such as powerbanks) in their carry-on luggage. Flight attendants can easily intervene in case of fire.
For now, this technology still requires refinement before commercial use. We will likely see lithium-sulfur batteries powering our electric cars in the future!
Also read: Electric vehicle batteries: Two new projects underway!
This page is translated from the original post "Stellantis investit dans les batteries en Lithium-Soufre avec Lyten" in French.
We also suggestthese articles:
Also read